What is Pump Technology? Understanding Its Types and Applications Explained
In the realm of engineering and industrial processes, pump technology plays a pivotal role in fluid management and transportation. Understanding the various types of pumps and their applications is essential for optimizing performance in a wide range of sectors, including manufacturing, agriculture, and water treatment. With advancements in pump technology, engineers and operators are now equipped with more efficient, reliable, and versatile solutions that cater to diverse operational needs.
The landscape of pump technology encompasses a plethora of designs, each tailored for specific functions and fluid types. From centrifugal pumps that ensure rapid movement of liquids to diaphragm pumps that handle viscous materials, the choices are vast. This introduction aims to delve into the fundamental concepts of pump technology, exploring its significance and the various classifications of pumps that have emerged over time. By understanding these elements, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions that enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall system efficacy. Whether for industrial applications or domestic needs, the advancement in pump technology continues to shape the way we manage fluids in our daily lives.

Types of Pumps: An Overview of Common Categories in Pump Technology
Pumps play a crucial role in various industries by moving liquids, gases, or slurries through systems. Understanding the types of pumps is fundamental to selecting the right technology for a specific application. Generally, pumps can be categorized into two main types: positive displacement pumps and dynamic pumps.
Positive displacement pumps operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it into the discharge pipe. This type includes gear pumps, diaphragm pumps, and piston pumps, which are commonly used in applications requiring precise flow control and high viscosity handling. On the other hand, dynamic pumps, such as centrifugal pumps, rely on rotational energy to impart velocity to the fluid, converting kinetic energy into pressure. These pumps are often utilized in applications that require high flow rates and are particularly effective for transporting low-viscosity liquids.
Each pump type has its unique advantages and is suitable for specific needs. For instance, positive displacement pumps are ideal for chemical processing industries where fluid characteristics vary, while centrifugal pumps are prevalent in water treatment and irrigation systems due to their efficiency and simplicity. Understanding these common categories helps engineers and technicians make informed decisions about the most effective pump technology for their unique applications.
Pump Technology: Types and Applications
Applications of Pump Technology: Industries and Processes Utilizing Pumps
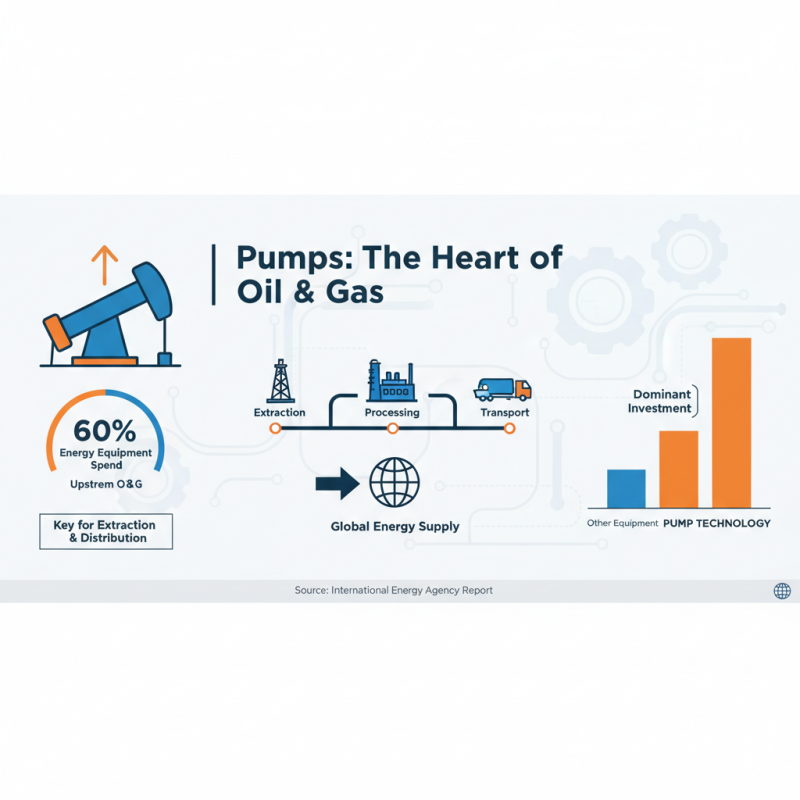
Pumps are essential devices used across various industries for transporting fluids efficiently. In the oil and gas sector, for instance, pumps facilitate the movement of crude oil and refined products through pipelines and processing plants. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, approximately 60% of all energy-related equipment expenditures are attributed to upstream oil and gas activities, with a significant portion devoted to pump technology. These pumps enable not only the extraction but also the distribution of hydrocarbons, ensuring a steady supply to meet global energy demands.
In the water and wastewater management industry, pumps play a crucial role in both treatment facilities and distribution systems. The global market for water and wastewater pumps is projected to grow from USD 35.6 billion in 2020 to USD 53.6 billion by 2027, as reported by MarketsandMarkets. This growth is driven by increasing urbanization, requiring efficient water management solutions to ensure safe drinking water and effective sewage treatment processes. For instance, centrifugal and positive displacement pumps are commonly used to move large volumes of water through treatment plants, demonstrating their importance in maintaining the health and safety of communities globally.
Additionally, in the food and beverage industry, pumps are utilized to handle various process liquids, including sauces, dairy products, and beverages. A report from the Food Processing Industry indicates that the need for hygienic pumps is on the rise, emphasizing the importance of maintaining product quality and safety standards. The use of specialized pumps that meet strict regulatory requirements ensures that these essential food products are processed without contamination, illustrating the diverse applications and critical nature of pump technology in modern manufacturing and service industries.
Mechanisms of Pump Operation: How Different Types Function
Pump technology is a vital component in various industries, playing a crucial role in fluid management. Understanding the mechanisms behind different types of pumps is essential for optimizing their application.
There are several categories of pumps, including centrifugal, positive displacement, and diaphragm pumps, each operating based on distinct principles.
Centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy to move fluids through centrifugal force, making them highly effective for applications requiring high flow rates and low viscosity fluids. According to industry reports, centrifugal pumps account for approximately 80% of the pump market, highlighting their dominance in applications ranging from water supply to chemical processing.
In contrast, positive displacement pumps, including gear and piston types, function by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge. This mechanism is particularly advantageous for handling viscous fluids and maintaining consistent flow rates irrespective of pressure changes.
The market for positive displacement pumps is projected to grow significantly, with expert analyses predicting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 5.3% over the next five years.
Lastly, diaphragm pumps, which utilize a flexible diaphragm to create a vacuum and move fluids, offer unique benefits in applications requiring gentle handling and minimal shear stress, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Each type of pump serves specific operational requirements, making knowledge of their mechanisms crucial for engineers and operators in the pursuit of efficiency and reliability in fluid management.
Advancements in Pump Technology: Innovations and Future Trends
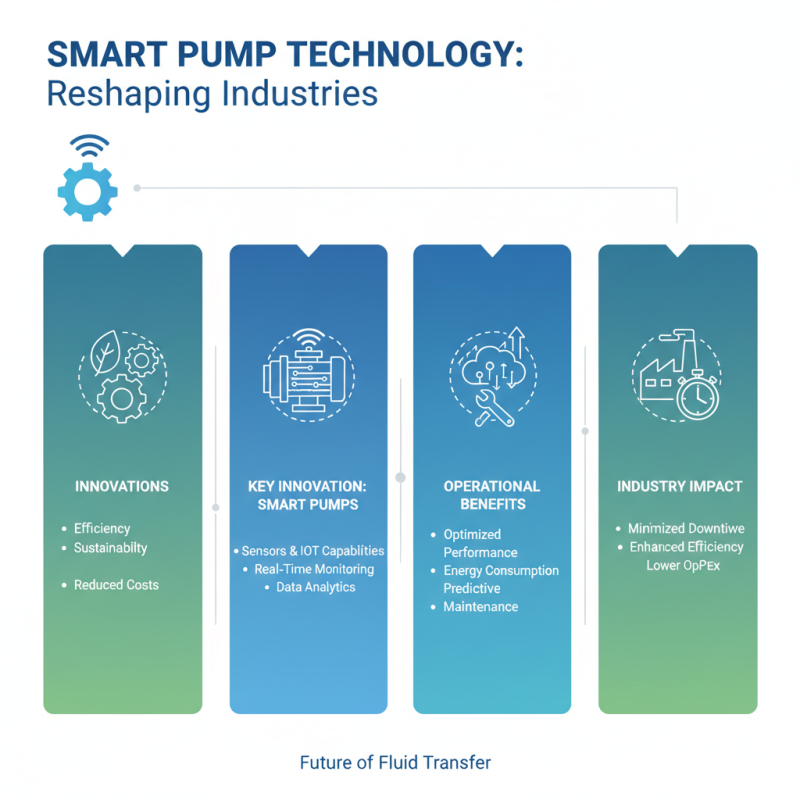
Recent advancements in pump technology have reshaped various industries, driving efficiency and sustainability. One of the most significant innovations is the development of smart pumps, equipped with sensors and IoT capabilities. These pumps offer real-time monitoring and data analytics, enabling operators to optimize performance, reduce energy consumption, and anticipate maintenance needs. This intelligence not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to minimizing downtime and operational costs.
Furthermore, advancements in materials science have led to the creation of pumps that can handle more aggressive fluids and operate in extreme environments. Enhanced corrosion resistance and durability are crucial, especially in sectors such as oil and gas or chemical processing. The future trend of integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, into pump systems is also on the rise, promoting eco-friendly practices and reducing the carbon footprint. As these technologies evolve, the potential for innovative applications expands, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable pumping solutions across various fields.
Choosing the Right Pump: Factors to Consider for Optimal Performance
When selecting the right pump for your application, several factors must be taken into consideration to ensure optimal performance. The first crucial aspect is the type of fluid being pumped. Different fluids have varying viscosities, chemical compositions, and temperature ranges, which can significantly impact the pump's efficiency and longevity. It’s essential to identify whether the pump will handle clean water, sludge, corrosive chemicals, or high-viscosity materials, as each requirement will influence the design and technology of the pump chosen.
Another important factor is the required flow rate and pressure. Understanding the system's specific requirements for flow is vital. Whether the application demands a constant flow or variable flow rates should guide the decision-making process. Additionally, the pressure at which the pump operates is pivotal to ensuring that the entire system functions effectively without causing damage to the pump or associated equipment.
Other considerations include the pump's power consumption, maintenance needs, and installation space. By carefully evaluating these elements, users can choose a pump that not only meets their operational needs but also promotes efficiency and cost-effectiveness over time.
Related Posts
-
Essential Tips to Effectively Back Up Your Sump Pump System
-

Understanding Sump Pumps in Basements: Key Statistics and Trends for Homeowners in 2023
-

How to Choose the Best Basement Drainage System for Your Home in 2025
-

2025's Top 10 Sump Pump Backup Systems for Ultimate Flood Protection
-
How to Choose the Right Sump Pump Check Valve for Your Home Needs in 2025
-
How to Effectively Pump Basement Water and Prevent Future Flooding
